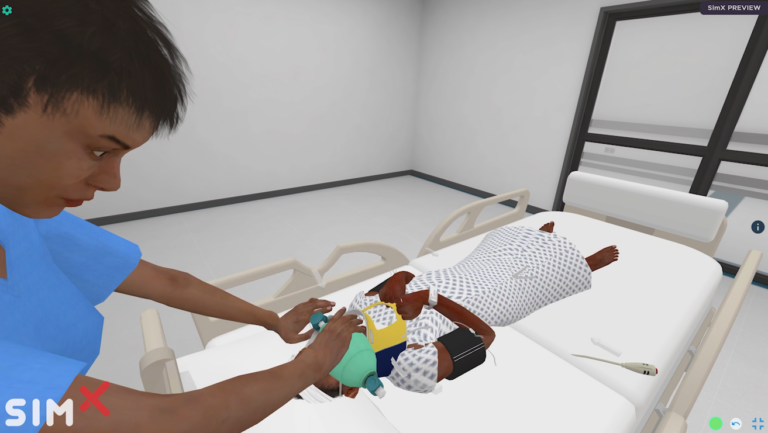
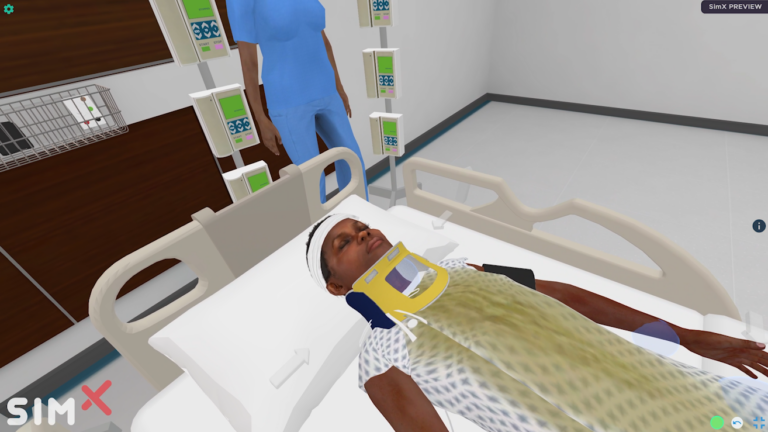
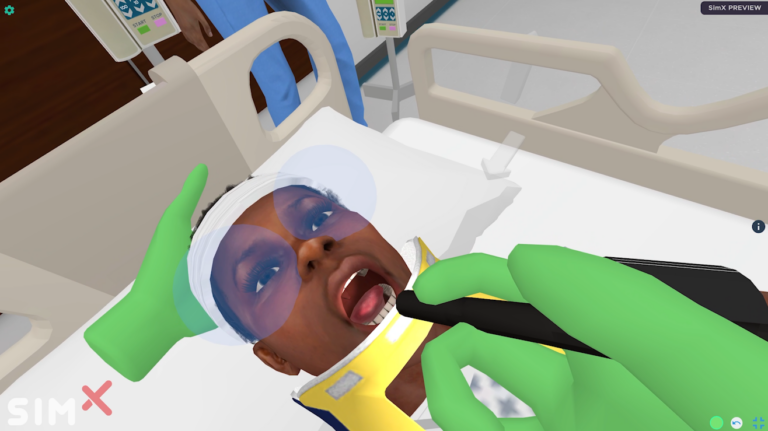
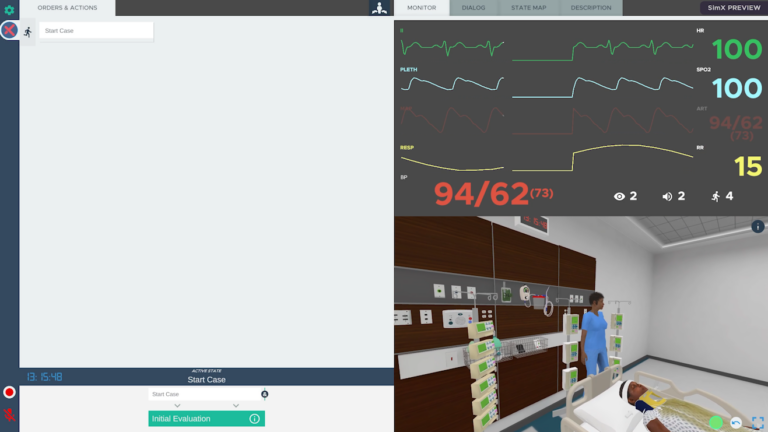
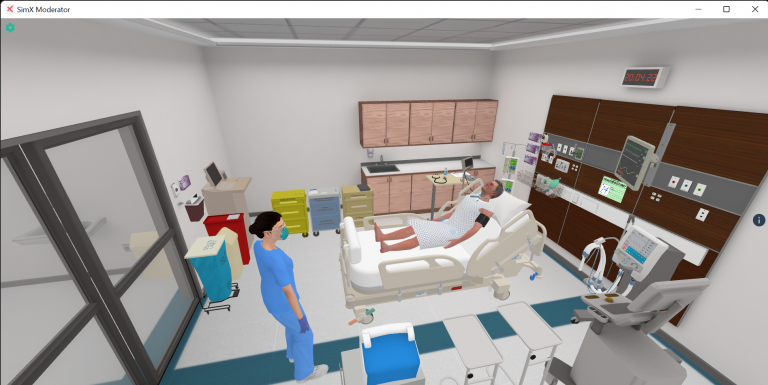
A 10-year-old male who presented after trauma with subdural hematoma who develops increased intracranial pressure.
Learning Objectives
1. Learners will recognize the signs of increased intracranial pressure.
a. Learners will examine the patient and find him to be minimally arousable (moaning when stimulated rather than answering coherently), initially with equal and reactive pupils, but over the course of the case will become unarousable and have unequal pupils. If actions are not performed soon enough, the patient will develop posturing and seizures.
2. Learners will demonstrate the initial emergency treatment of increased intracranial pressure.
a. Learners will raise the head of bed to 30 degrees, straighten the head, and give IV mannitol or 3% hypertonic saline. They will perform bag mask ventilation to hyperventilate the patient, and prepare to intubate the patient. They will ask for vital signs and ask for labs to confirm that sodium and glucose are normal.
3. Learners will recognize the need to call for additional help/resources.
a. Learners will call for neurosurgery in order to perform either a decompressive craniotomy or place an invasive ICP monitor.
MINIMUM:
OS: Windows 10
Processor: Intel Core i5-2300 | AMD FX-4350
Memory: 4 GB RAM
Graphics: Nvidia GeForce GTX 2060
DirectX: Version 11
Storage: 12 GB available space
RECOMMENDED:
OS: Windows 10
Processor: Intel Core i7-2300 | AMD FX-4350
Memory: 8 GB RAM
Graphics: Nvidia GeForce GTX 3060
DirectX: Version 11
Storage: 12 GB available space
Interested in this scenario?
Sign up to talk with a member of the SimX team today!